Double Glazed Windows
- Home
- Double Glazed
- Double Glazed Windows
What Are The Double Glazed Windows?
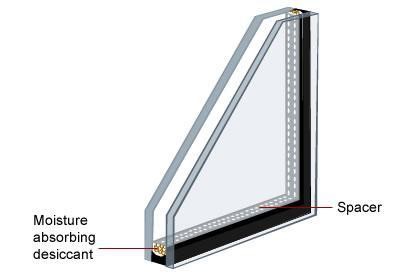
Double glazed windows are two panes of glass sandwiched together with a spacer in between. The space between the two panes is the cavity and the air is vacuumed and sealed. This is called a Double Glazed Unit.
The cavity is filled with argon gas, improving the heat and cold temperature transfer 1000 fold. This low-maintenance addition does not require any refilling throughout the window’s life.
We offer double glazed windows with Aluminium Frames or Thermally Broken Aluminium to suit your needs. Ask us to show you the differences.
Benefits Of Double Glazed Windows
Makes your space more comfortable
You use air conditioning and heating to maintain the temperature of your home. However, double glazed windows reduce the need for an external air conditioner, so you feel comfortable throughout the year.
Every bit of floor, corner and even air is yours. The outside environment becomes part of your home, and you realise you are a part of nature.
Restores peace and calm in your home
The atmosphere in your home makes or breaks your mood. Why not make the place where you choose to dwell in comfort your heavenly place? With double glazed windows, you get that comfortable feel right where you live.
It creates harmony and calmness and invites the environment to blend as one. The ambient temperature gives homes and offices a sheer comfort not understood until you live with double glazing.
Be warmer in winter and cooler in summer
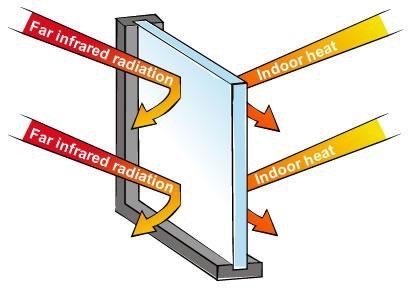
The sealed air gap between the two panes is an added insulation layer. This thermal resistance reduces heat escaping in winter to keep your home at a more comfortable temperature. Double glazing has the reverse effect in summer, preventing unwanted heat from entering the house.
When you are nearby a window, your comfort is affected by the temperature of the glass. With double glazing, the unwanted outside temperature doesn’t transfer through, leaving the inside pane close to room temperature.
Double glazed windows lower your energy bills
Minimise the noise with the double glazed windows
Double glazed windows are the ideal energy-efficient choice with the added benefit of minimising noise. Sealed double glazing effectively reduces medium to high-frequency noise, such as the human voice. A difference in glass thickness between the inner and outer panes improves sound reduction even further.
Reduce condensation and mould
Double glazing also reduces condensation, which can result in the unhealthy formation of mould.
Increase your home security with the double glazed windows
Double glazed windows are a safer option when compared to standard single-pane windows. The two layers of glass are a minimum of 5mm toughened glass, and the argon gas filling acts as a cushion if something hits the outer glass. Specify toughened or laminated glass or add Stainless Steel Security Screens to increase your security level even more.
What To Look For Double Glazed Windows
Amount of space between panes
The typical space between panes ranges from 6mm to 20mm. Although a minimum width of 6mm is ok, 12mm is recommended for optimum thermal performance.
Alternatively, for acoustic control or to reduce low-frequency noise, such as traffic and aircraft, the optimum air gap recommended is 100mm or over. Note that such large gaps allow convection to occur between the panes and reduce the insulating performance.
For better energy-efficient performance, choose double glazing with a space of 10 to 20mm between the panes.
Double Glazed Windows - What’s In Between
Amount of space between panes
Because the space between the panes in double glazed windows is fully sealed, it acts as an insulator, limiting the transfer of cold air into your home.
Thermal and acoustic performance can also be increased when gas fills this space. The most popular gas used is argon which has low conductivity properties and is 1000 times better than air for insulation.
Inert, low-conductivity gas inserted between panes will increase performance.
Double-glazed units include a metal or polymer strip spacer separating the two glass panes. Typically, spacers contain a desiccant (drying agent) to remove moisture trapped in the air space.
Type of glass used
A wide range of glass types, such as low-E and laminated, can be used in double-glazing units to further increase energy efficiency and manage noise control.
Low-E glass will further reduce the amount of heat escaping, while thicker laminated panes disrupt sound waves to improve acoustic performance.
Common problems
Windows need to be considered as a whole unit. The framing material you choose to complement your glass may enhance its performance or, in some cases, reduce its energy-efficient properties.
Standard aluminium window frames readily conduct heat and cold and, if not thermally enhanced, may eliminate any benefit from installing expensive double glazing.
How well the cavity is sealed and the type of spacer used are also important factors to consider. If the double-glazed unit is not sealed correctly or the spacer does not contain adequate desiccant, it can reduce performance and condensation will appear on cold surfaces.
Advantages
- Minimises heat loss in winter
- Minimises heat gain in summer
- Improves acoustic performance
Disadvantages
- Higher cost than single glazing
Low-E Glass
Low-E is a standard clear glass that has a special coating on one surface. Low-E refers to low emissivity, the capacity of a surface to radiate heat. Emissivity is measured on a scale from 0 to 1, with 1 representing the highest emissivity.
The benefits of low-E glass
Low-E glass can reduce the amount of heat conducted through the glass by around 30% compared to ordinary glass. Low-E glass further improves thermal efficiency by cutting glare and preventing damage to interior furnishings caused by ultraviolet rays.
Newer generation low-E often uses laminated and toned glass combinations to provide superior performance over the non-coated glass.
The most comprehensive solution is found by combining a low-E coating with double glazing. A low-E coating and a suitable frame can stop up to 70% heat loss and 77% heat gain compared to standard 3mm glass.
Hard or soft coat low-E glass
There are two types of low-E glass: hard coat (online) and soft coat (offline). Hard coat low-E glass is made by coating the glass during production with a thin metallic oxide layer, effectively welding it to the glass surface.
Soft coat low-E glass, or sputter coating, is applied to glass that has already been formed. The glass enters a vacuum chamber filled with an inert gas that is electrically charged.
The electricity combined with the vacuum allows molecules of metal to sputter onto the glass. This process provides the highest level of performance and a nearly invisible coating.
Hard coat low-E glass is the more common variety. It is durable and difficult to scratch and can be used for single-glazed applications. On the downside, it has higher U-values than soft coat low-E glass and slightly higher haze levels.
On the other hand, soft-coat low-E glass is less common as it allows more visible light with less visible haze. Its ultra-low emissivity also provides excellent U-values.
The downside of soft coat low-E glass is that it can only be used in double glazed windows and may have slight colour variations. The soft coat is also less durable than the hard coat.
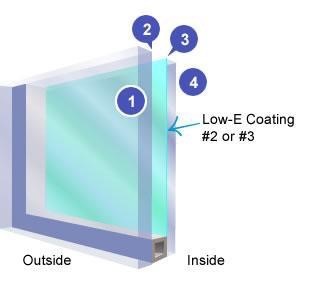
Which side of the glass to coat
The effectiveness of low-E glass depends on the direction the coating is facing. We recommend that the low-E coating be placed on the inside-facing surface for single-pane windows.
Low-E coatings are sensitive to weather and pollutants, making them difficult to clean without damaging the surface.
With double glazed windows, low-E glass can be specified on a particular side of the glass, depending on what you want to achieve.
In warmer climates where summer heat reduction is a priority, the coating should be on the inside-facing surface of the outside pane (surface #2). This will minimise heat coming into the home by absorbing solar radiation and reflecting it away.
In colder climates where heat retention is a priority, the coating works best by facing outwards on the inside pane (surface #3). The coating will work by absorbing inside heat and reradiating it back into the room.
Common problems
Low-E glass reduces solar gain in winter as well as summer. For this reason, it is not recommended for solar control in colder climates when the winter sun provides valuable natural heating.
It is more beneficial to use low-E glass with double glazing only to reduce winter heat loss.
Advantages
- Improves solar and thermal control
- Reduces summer heat gain and winter heat loss
- Decreases UV transmission such as furniture fading
- Reduces condensation in double glazing
Disadvantages
- Must be applied correctly
- Expensive option
- Can reduce valuable solar heat gain in colder climates

